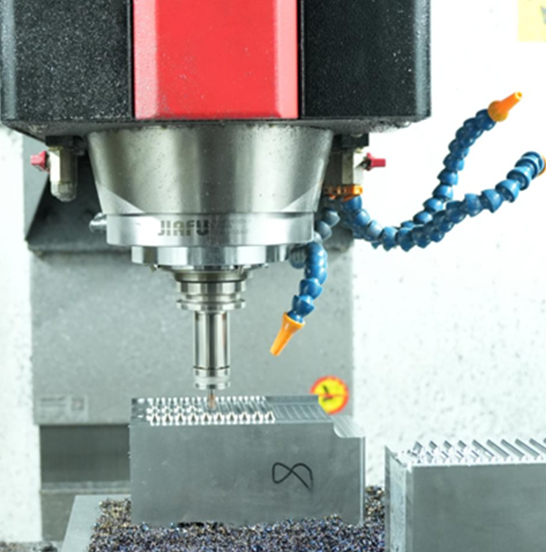
YOUR ONE-STOP DIE CASTING MOLD MANUFACTURING
Expert Die Casting Mold Manufacturer in China – JUFENG Precision
High-quality die casting molds are essential for precision aluminum die casting production.
JUFENG Precision is a leading aluminum die casting and mold manufacturer in China, specializing in high-performance die casting molds and components. With extensive expertise and advanced manufacturing capabilities, we deliver durable, cost-effective molds tailored to meet strict industry standards and customer specifications.
As a trusted China die casting mold supplier, JUFENG Precision excels in providing reliable tooling solutions and premium aluminum die cast parts for global clients. Our commitment to innovation and quality ensures superior performance and efficiency in every project.

Product Gallery: Die Casting Molds

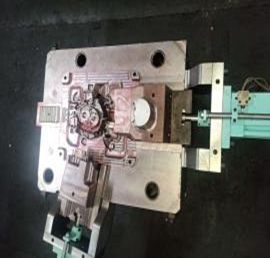




Expert Die Casting Mold Manufacturing Capabilities | JUFENG Precision
Our in-house aluminum die casting mold production ensures reliable solutions for diverse project requirements.

Advanced Mold Validation & Simulation Technology
Our engineering team employs cutting-edge mold flow analysis and simulation technologies to optimize die casting mold performance. Utilizing industry-leading software including:
• AnyCasting for precise filling simulation
• CREO/Pro-Engineer for 3D modeling
• AutoCAD for technical drawings

Professional Die Casting Mold Design Team
Our expert engineering team delivers comprehensive mold design solutions:
• Concept development & 3D visualization
• Advanced functional analysis
• Precision mold flow simulation
• Complete tooling design packages

In-House Die Casting Mold Solutions
As a leading China die casting mold manufacturer, JUFENG Precision provides complete in-house capabilities:
• Mold Design & Engineering
• Precision Mold Manufacturing
• Rigorous Mold Validation
• Lifetime Maintenance Services



Where Do Your Die Cast Molds Come From?

Die casting mold manufacturing

Die casting mold manufacturing

Die casting mold manufacturing
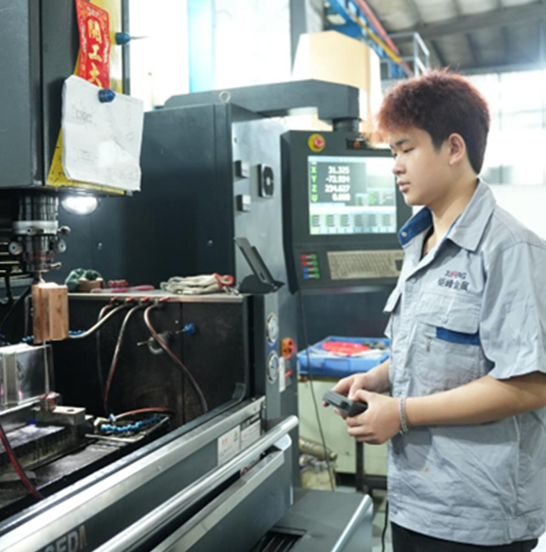

Die casting mold manufacturing
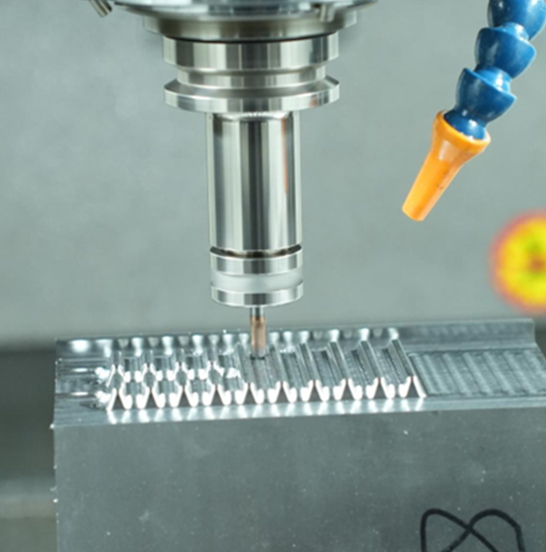

Die casting mold manufacturing

